Blockchain technology, originally developed as the underlying system for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, has far-reaching implications beyond digital currencies
Its decentralized, transparent, and secure nature makes it an ideal solution for many industries, particularly supply chain management. Supply chains are complex networks involving multiple stakeholders, from suppliers and manufacturers to distributors and retailers. Ensuring transparency, traceability, and security within these networks is crucial but challenging. Blockchain technology addresses these challenges by providing a distributed ledger that records all transactions immutably and transparently, fostering trust and collaboration among stakeholders.
One of the primary applications of blockchain in supply chain management is enhancing transparency and traceability. Traditional supply chains often suffer from information silos, where data is fragmented and inconsistently shared among participants. This lack of transparency can lead to issues such as counterfeiting, fraud, and inefficiencies. Blockchain technology solves this by creating a single, immutable record of transactions that all participants can access. Each transaction, from the sourcing of raw materials to the delivery of finished products, is recorded on the blockchain. This ensures that all stakeholders have a consistent view of the supply chain, reducing the risk of discrepancies and fraudulent activities.
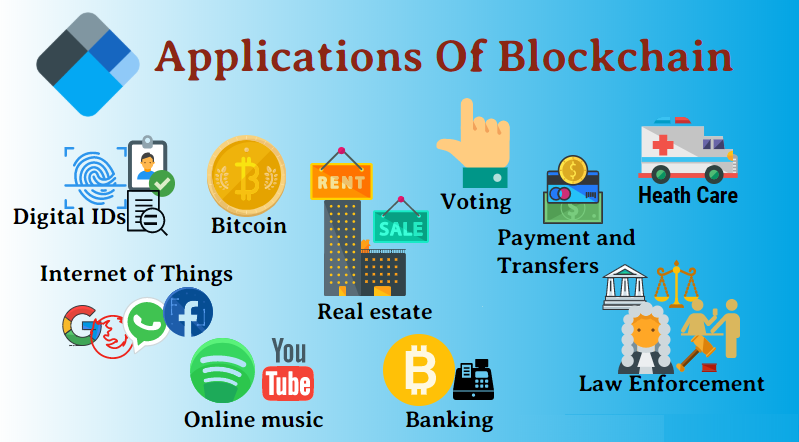
For instance, in the food industry, blockchain can track the journey of food products from farm to table. This level of traceability allows consumers to verify the origins of their food, ensuring it meets safety and ethical standards. In the event of a contamination issue, blockchain enables quick identification of the affected batches, facilitating faster recalls and minimizing harm
#1.Improving Efficiency and Reducing Costs
Blockchain technology also enhances supply chain efficiency by automating processes and reducing administrative burdens. Smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code, play a crucial role in this aspect. These contracts automatically enforce the agreed-upon rules and conditions, eliminating the need for intermediaries and manual interventions. For example, a smart contract could automatically release payment to a supplier once the goods have been delivered and verified.
Additionally, blockchain reduces the need for extensive paperwork and documentation. Traditional supply chains often involve numerous documents, such as invoices, purchase orders, and bills of lading. Managing these documents manually is time-consuming and prone to errors. By digitizing these documents and recording them on the blockchain, companies can streamline their operations, reduce paperwork, and minimize errors, leading to significant cost savings.
#2. Enhancing Security and Reducing Fraud
Supply chains are vulnerable to various security threats, including data breaches, counterfeit products, and unauthorized access. Blockchain's cryptographic security measures provide robust protection against these threats. Each transaction on the blockchain is encrypted and linked to the previous transaction, creating a secure and tamper-proof chain of records. Any attempt to alter a record would require altering all subsequent records, which is practically impossible without consensus from the network participants.
This heightened security is particularly beneficial for industries dealing with high-value goods, such as pharmaceuticals and luxury items. For example, in the pharmaceutical industry, counterfeit drugs pose a significant threat to patient safety and brand integrity. By recording every step of the drug production and distribution process on the blockchain, companies can ensure the authenticity of their products and quickly identify any instances of counterfeiting.
#3. Fostering Collaboration and Trust
Blockchain technology fosters collaboration and trust among supply chain participants by providing a transparent and immutable record of transactions. Traditional supply chains often suffer from mistrust among stakeholders due to the lack of visibility into each other's operations. Blockchain addresses this issue by ensuring that all participants have access to the same, unalterable information. This transparency builds trust, as stakeholders can verify the accuracy of the data and ensure that everyone is adhering to the agreed-upon terms and conditions.
#4.Blockchain is Important in Supply Chain
This transparency builds trust, as stakeholders can verify the accuracy of the data and ensure that everyone is adhering to the agreed-upon terms and conditions.
- Enhanced Transparency and Traceability:
Blockchain provides a single, immutable record of transactions accessible by all participants, ensuring consistency and reducing the risk of discrepancies and fraud.
It allows for tracking the journey of products from origin to consumer, enhancing trust and enabling quick identification of issues such as contamination.
- Improved Efficiency and Reduced Costs:
Smart contracts automate processes, enforce rules, and eliminate the need for intermediaries, reducing administrative burdens and manual interventions.
Digitizing documents and recording them on the blockchain streamlines operations, reduces paperwork, and minimizes errors, leading to significant cost savings.
- Enhanced Security and Reduced Fraud
Blockchain's cryptographic security measures provide robust protection against data breaches, counterfeit products, and unauthorized access.
It ensures the authenticity of high-value goods, such as pharmaceuticals and luxury items, by recording every step of the production and distribution process.
Supply chains are vulnerable to various security threats, including data breaches, counterfeit products, and unauthorized access. Blockchain's cryptographic security measures provide robust protection against these threats. Each transaction on the blockchain is encrypted and linked to the previous transaction, creating a secure and tamper-proof chain of records. Any attempt to alter a record would require altering all subsequent records, which is practically impossible without consensus from the network participants.